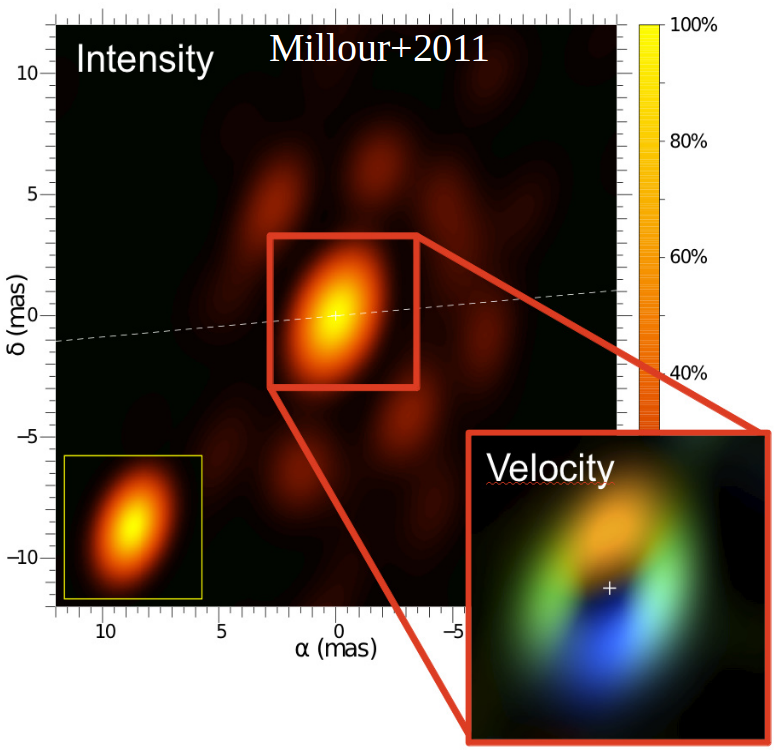
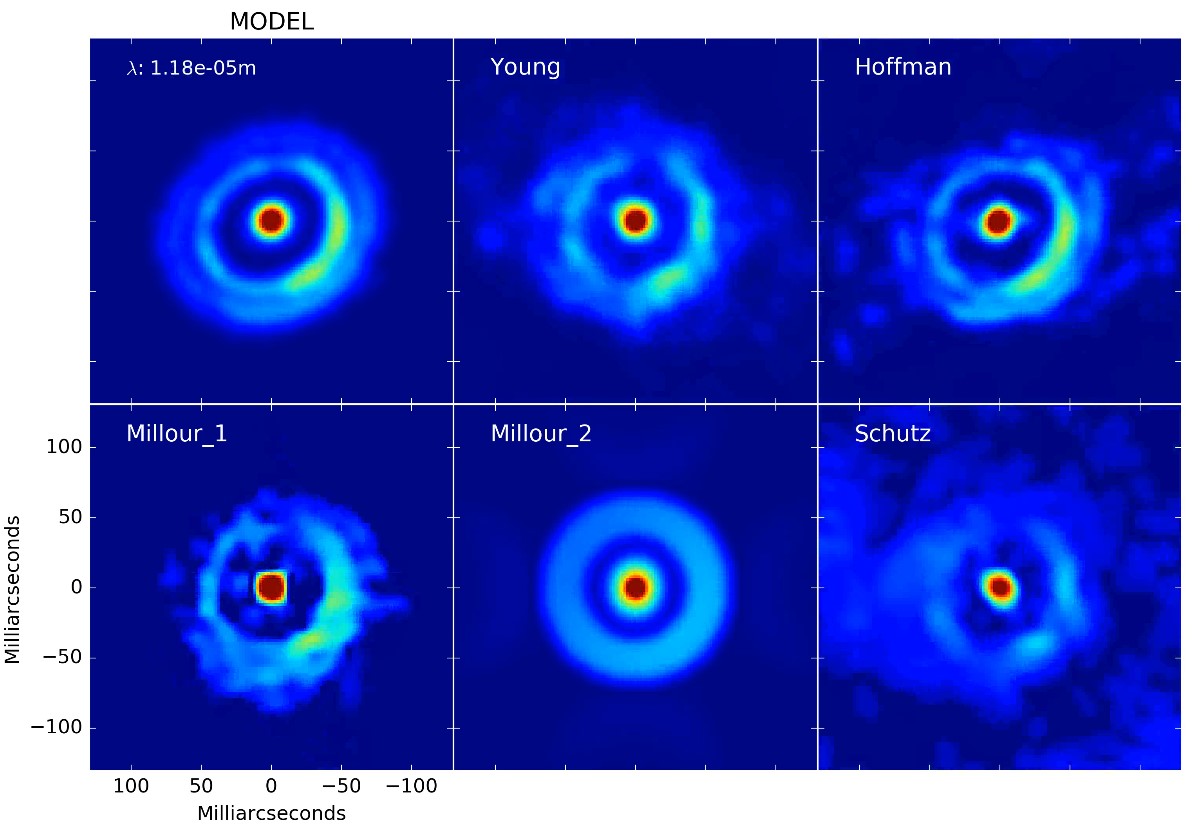
HD 62623 is a hot, massive star of spectral type A (i.e. with a temperature around 10 000 Kelvin). It is one of the few stars of its kind which hosts dust in its environment. Such a hot and massive star is not expected to host dust in its vicinity. We managed to disentangle the gas from the dust around this supergiant star using interferometric imaging with the Very Large Telescope Interferometer. The corresponding image cube is the first one to be reconstructed from optical interferometric data. The obtained image enables us to confirm that there is an unseen companion star very close to the central star, which is probably at the origin of the circumstellar disk.
You can see the joint press releases by browing the following links :
- Press release from CNRS (French)
- Press release from the Max-Planck Institute (English)
- Press release from the Max-Planck Institute (German)
- Announcement from ESO (English)
and also the press coverage (will be updated from time to time) :
- Astronews website (German)
- Universe today (English)
- Cmarchesin (English)
- link2universe (Italian)
- News in nederlands
- techno-sciences.net (French)
- Physorg.com (English)
- science.compulenta.ru (Russian)
- maxisciences (French)
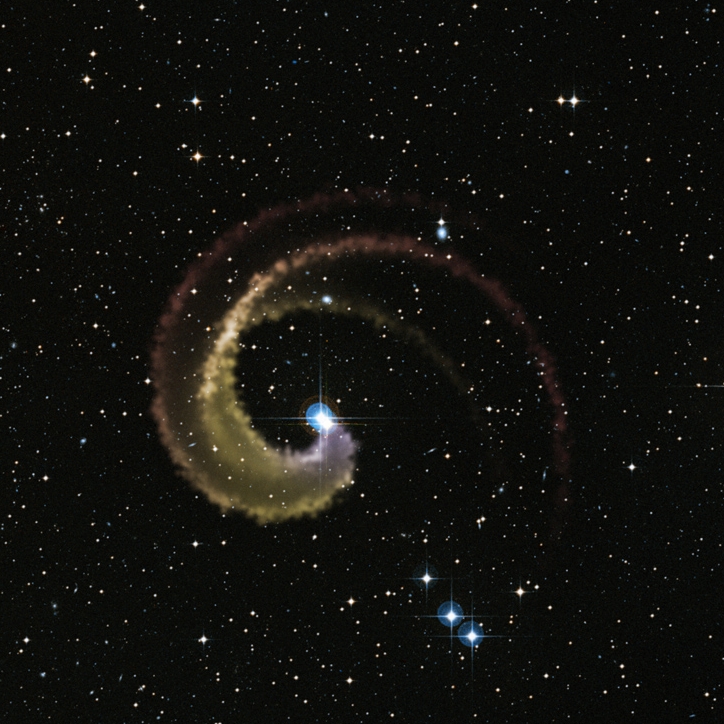
The system could look like this impression:

This picture illustrates the appearance of HD62623 as seen through the AMBER instrument.
The data of this paper is made avalaible in HD62623 AMBER dataset.


















Commentaires récents